¶ Introduction
Toileting refers to the act of having a bowel movement or urinating into a suitable receptacle.
Muscle weakness caused by ALS affects the ability to get to a toilet, both in general, and in a timely manner. Adaptive equipment and alternative approaches can aid in toileting.
¶ Types of Toilets
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Bedpan | A shallow container used for urination or defecation while lying down. |
| Commode Chair | A portable toilet, often resembling a chair, often with a removable container for catching waste. |
| Flush Toilet | A plumbing fixture that disposes of human waste by using water to flush it through a drainpipe to a sewer or septic system. |
| Urine Bottle | A portable container used for urination. |

A bedside commode chair.
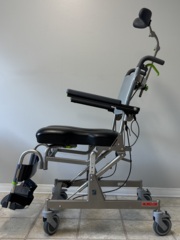
A wheeled tilt shower commode chair, side view, upright.
¶ Transferring to a Toilet
Clothing on the lower body should be removed before sitting on a toilet or commode chair. It is far more difficult to remove clothing whilst already sitting. There is a risk of falling off the toilet when leaning side-to-side to remove clothing.
¶ Walking
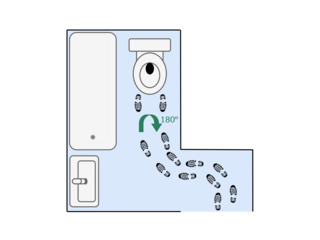
Flush toilets are typically mounted near walls; this necessitates either a turn in order to reach them before sitting down, or in some cases, walking backwards for a few steps. These maneuvers are difficult and potentially unsafe for someone with significant ALS disease progression.
Grab bars and transfer poles may be used to provide support while walking backward to a toilet if the individual retains a moderate amount of lower limb strength.
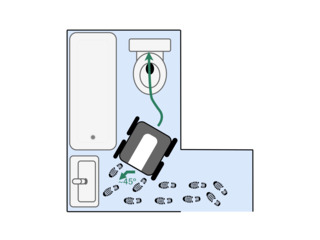
Wheeled over-the-toilet commode chairs may be used to complete the journey to the toilet if the layout of the bathroom permits. Care should be taken to avoid ramming the commode chair into the toilet tank, as it may cause it to crack.
Use of a wheeled commode would almost certainly require an assistant to help set and release the brakes.
It may not be possible to transport the commode chair to a toilet in some cases. If so, most commode chairs can be fitted with a pan that catches waste, which can then be thrown out or flushed down a toilet.
¶ Using a Transfer Board
A transfer board may be used to transfer from a wheelchair to a commode chair.
Transfer boards should not be used to transfer directly to a conventional flush toilet. The seats on flush toilets are not designed to withstand the lateral loading a transfer board may place on them. It is possible for the seat to break off of the toilet during a transfer. A commode chair with stable legs may be placed over top of the toilet instead.
¶ Using a Lift
A floor lift must be able to navigate to the toilet safely, and have enough room for an attendant to provide assistance.
Use of a lift for the purpose of toileting on a commode chair or conventional flush toilet is only practical if it is possible to use a sling that has an open (or mostly-open) bottom. Otherwise, the effort needed to remove the sling is comparable to that of attempting to remove clothing while seated.
A patient using a lift for toileting is likely not suitably strong enough to undress safely while sitting on the toilet, even with the help of an assistant.
The patient should be undressed from the waist down when they become airborne during a lift transfer. This way, when they land on the toilet or commode chair, they will be ready to go about their business, other than perhaps making minor adjustments to get parts of the sling out of the way.
Clothing which is compatible with using a lift for toileting includes:
- side-zip pants, specifically, the kind that unzips starting at the waist and heading to the ankle
- skirts or robes that are partially removable while sitting in the wheelchair, such that the sling can be fit between the patient and the garment
With an appropriate sling and clothing, the procedure for toileting with a lift becomes:
- Open the clothing in such a way that the sling can be placed in direct contact with the patient
- Raise the patient with the lift
- Remove any clothing that has caught on the sling
- Complete the transfer
- Move any parts of the sling that are in the way of successful evacuation out of the way, or if desired, remove the sling entirely
Returning to the wheelchair after using the bathroom can prove difficult, especially with respect to dressing. Transferring to a bed is desirable if possible, as the attendant will be able to more easily dress the patient and then transfer them back to the wheelchair.
It may be possible to position the pants or robes on the wheelchair in such a way that dressing on the wheelchair itself is possible. Note that doing so often requires that the clothing in question be oversized so that there is a great deal of margin for errors in positioning.
Use a bed for dressing after toileting whenever possible.
¶ Sitting on a Toilet
¶ Stability and Comfort
Sitting on a toilet for a prolonged length of time requires sufficient trunk strength to maintain stability. Those with significant muscle wasting in their gluteus muscles may become sore from sitting on a rigid toilet seat.
A padded toilet seat or a commode chair with a padded seat increases comfort.
Commode chairs with a back rest, lumbar, and leg supports on the sides provide support when trunk strength is low.
¶ Seat Height
Toilets come in different seating heights. While there are height measurements that are quite common, toilets may be installed at any height.
Ideally, a person's knees would be higher than their hips when sitting on a toilet. Such a position helps with evacuation.
Lower limb weakness necessitates the use of a toilet with a higher seating position, as low seating positions require significant strength to stand up from. Further disease progression will require ever-higher seating heights, until it becomes impractical to stand independently from any height.
Toilet seat risers or over-the-toilet commode chairs (with or without wheels) can be used to increase the seating height of a flush toilet.
Grab rails may be useful if the toilet itself already has a relatively high seating position.
¶ Hygiene
¶ Toilet Paper
Wiping with toilet paper requires being able to sufficiently hold the wad of paper while controlling its motion. It must also be possible to reach back far enough to position it properly.
Adaptive equipment for continued use of toilet paper is limited. There are wands that can be used which are held in front of the body and reach under to the target area. However, the weight of the wand may be too much to overcome, and operating it still requires a modest amount of grip strength, much like wiping directly without it. They may also be difficult to reload for multiple wipe passes. These wands are more suited to those that still have good use of their hands, but are unable to reach behind themselves.
Personal Experience: Wiping technique with very weak hands
I got away with the following for many months. My clean underwear suggests that it was a success, I guess.
- Make a generously sized wad of toilet paper.
- Place it in the right hand, especially over the fingertips, palm facing upward.
- Rest the hand on the right side of the toilet seat, palm still facing up.
- Sit on the hand, and use body and arm motion to move the hand forward and backward to wipe right on the target area.
It would usually take a few iterations, but it got the job done.
— Craig R, diagnosed with ALS at age 38
¶ Bidets
🚧
¶ Waste Disposal
Waste that is not being disposed of in a flush toilet will need to be disposed of according to the regulations of the municipal waste program. Some municipalities require signing up for a diaper removal program, which may have associated fees and require periodic renewal.
The waste disposal container should be at least 10 gallons (38L) in size if it is to be collected weekly.
¶ Example Setups
The following are complete examples of toileting with ALS.
Example 1: Moderate disability with walking and standing
Adaptive equipment:
- walker
- grab bars mounted near the toilet
- toilet seat riser, or over-the-toilet commode chair
Steps:
- Walk as close to the toilet as possible with the walker
- Use a wall-mounted grab-bar for support to turn around
- Undress as much as is necessary
- Slowly sit down upon the toilet (fitted with a seat riser)
Example 2: Significant disability with walking and standing
Adaptive equipment:
- side-zip pants; no underwear
- floor lift, open-bottom sling
- wheeled over-the-toilet commode chair
Steps:
- Prepare the waste collection tray on the commode chair, if not being placed over a flush toilet
- Unzip the pants all the way to the ankles
- Place the sling
- Raise the patient with the lift, remove clothing that may have got caught
- Complete the transfer to the commode chair
- Align the commode chair with the flush toilet, if applicable; set the brakes
- Adjust the sling as necessary to get it out-of-the-way, or remove it entirely
- "Use the bathroom"
- Perform hygiene tasks, such as wiping
- Return to the wheelchair by doing the previous steps in reverse
¶ Public Bathrooms
Public bathrooms, even those which are fitted with necessary adaptive equipment to meet disability standards bring with them some amount of risk when being used by an ALS patient. Risks include:
- Adaptive equipment such as grab bars being in poor condition
- Grab bars not being placed in an ideal location for the user's specific strength profile
- The toilet being at an inappropriate height for the user to be able to get on and off of it
- Flooring which differs greatly from that found at home; some patients may rely on a very specific amount of grip to perform the maneuver of standing back up from the toilet
A public bathroom should be evaluated for suitability before expecting to use it.
¶ Alternate Methods
¶ Remaining in a wheelchair
Males may be able to urinate while remaining in a wheelchair.
The patient may wear a condom catheter allowing them to simply urinate when the time comes.
Patients in a power wheelchair with an anterior (forward) tilt feature may use a urine bottle with the help of an assistant.
Equipment required:
- Power wheelchair with anterior tilt feature
- Side-zip pants with no underwear underneath
- Urine bottle
- Small washcloth
Steps:
- Unzip the pants, revealing the patient's entire lap
- Fasten the seatbelt, if it is not already
- Place the washcloth under the patient's private area, to absorb any dribble
- Place the urine bottle, and hold it firmly
- Till the seat of the wheelchair forward the least amount possible until everything lines up in such a way that urine will surely go into the bottle
- Urinate into the bottle
- When complete, carefully take away the bottle and dump it into a toilet
- Tilt the seat of the wheelchair to a neutral position
- Use the washcloth to clean up
- Zip the pants back up
¶ See Also
¶ Adaptive Equipment
- Toileting Aids Bedpans • Bidets • Toilet Seat Risers • Urine Bottles
- Commode Chairs
- Patient Lifts and Slings